- 1. 概念
- 2. Non-Local Operation
- 3. ASPP, PSPNet
- 4. Self-Attention
- 5. Object-Context Representation (OCR)
- 6. Criss-Cross Attention (CCA)
- 参考文献
1. 概念
上下文信息 (context), 长期依赖 (long-range dependencies), 注意力 (attention) 这些概念提出的目的都是希望我们的特征能够在卷积等局部操作的基础上, 更多的吸收图像全局的信息, 从而提高特征的判别性. 这些概念一开始在 NLP 任务中得到了广泛的思考, 比如 LSTM, Attention 机制 (因为自然语言是天然的序列, 长距离的特征依赖尤为明显), 而近年来人们发现在 CV 中对这些概念的扩展和应用也能极大的提高特征的表达能力.
早期的长期依赖都是通过不断地重复局部操作来实现的, 比如两个典型的例子:
- CNN 中, 通过多层卷积和下采样可以扩大高层卷积核的感受野
- RNN 中, 通过多次重复循环单元实现远距离信息的融合
2. Non-Local Operation
Non-Local 操作的一般形式是 Non-Local Network1 提出的:
\[\mathcal{y}_i = \frac1{\mathcal{C}(\mathbf{x})}\sum_{\forall j}f(\mathbf{x}_i, \mathbf{x}_j)g(\mathbf{x}_j),\]其中 \(f(\cdot, \cdot)\) 是二元函数, 用于计算 \(\mathcal{x}_i\) 和 \(\mathcal{x}_j\) 的相似度, \(g(\cdot)\) 是一个单元函数, 用于将 \(\mathcal{x}_i\) 投影到一个嵌入空间中计算新的特征.
2.1 二元函数 \(f(\cdot, \cdot)\)
该函数的一个基本性质是, 两个元素越相似, 函数值越大.
-
高斯函数:
\[f(\mathbf{x}_i, \mathbf{x_j}) = e^{\mathbf{x}_i^T\mathbf{x}_j}.\] -
嵌入的高斯函数:
\[f(\mathbf{x}_i, \mathbf{x}_j) = e^{\theta(\mathbf{x}_i)^T\phi(\mathbf{x}_j)}.\]这里的 \(\theta(\mathbf{x}_i)\) 和 \(\phi(\mathbf{x}_j)\) 可以是线性映射, 也可以是其他的复杂函数.
-
点积:
\[f(\mathbf{x}_i, \mathbf{x}_j) = \theta(\mathbf{x}_i)^T\phi(\mathbf{x}_j).\] -
拼接:
\[f(\mathbf{x}_i, \mathbf{x}_j) = \text{ReLU}(\mathbf{w}^T_f[\theta(\mathbf{x}_i), \phi(\mathbf{x}_j)]).\]
3. ASPP, PSPNet
在语义分割任务中, 在高层特征进行分类时, 结合多尺度的上下文 (Multi-Scale Context)信息是极其重要的. 目前比较流行的方法有:
- ASPP2: 通过一系列并行的不同膨胀率的膨胀卷积实现. 详见 DeepLab 系列.
- PSPNet3: 通过 Pyramid Pooling Module 在不同尺度的特征图上做常规卷积来捕获多尺度信息, 但是损失了特征图的精度. 详见 PSPNet 系列.
4. Self-Attention
Self-Attention4 通过计算目标 pixel 和其他所有 pixels 之间的关系作为 attention map (权重), 再通过特征的加权和来吸收上下文的信息.
\[\label{eq:ocr} \mathbf{y}_i = \rho(\sum_{s\in\mathcal{I}} w_{is}\delta(\mathbf{x}_s))\]其中 \(w_{is}\) 是像素 \(\mathbf{x}_i\) 和 \(\mathbf{x}_s\) 的关系. 详见 注意力机制.
5. Object-Context Representation (OCR)
OCR5 的 motivation 是表示图像中不同的 object, 然后每个 pixel 从 objects 的表示中吸收信息.
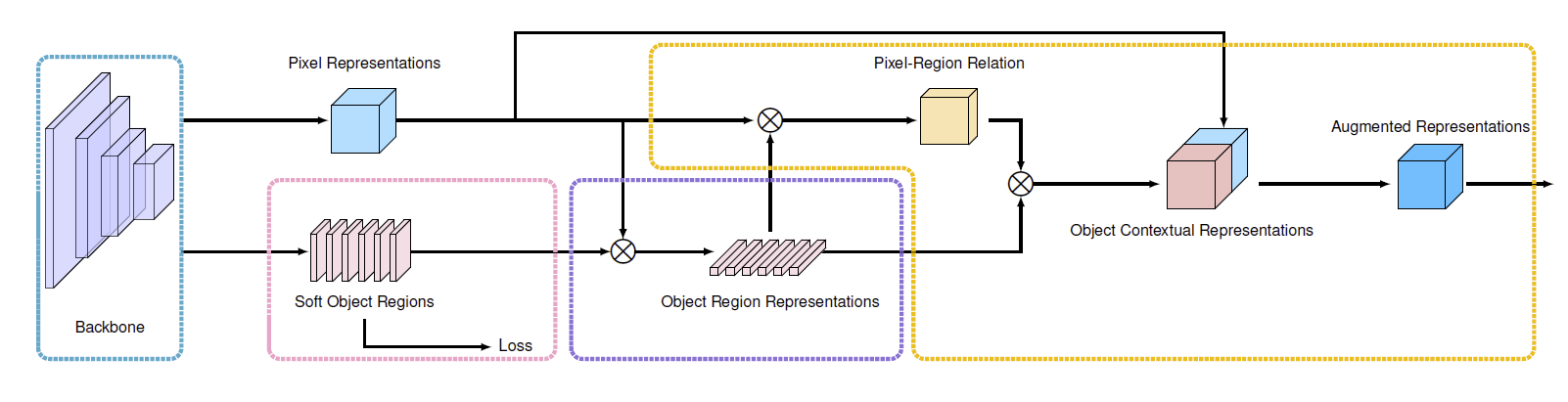
图 1. Illustrating the pipeline of OCR. (i) form the soft object regions in the pink dashed box. (ii) estimate the object region representations in the purple dashed box; (iii) compute the object contextual representations and the augmented representations in the orange dashed box.
5.1 Object 区域的表示
计算每个 pixel 属于某个 object 的权重, 然后把所有 pixel 的特征向量加权和作为 object 的表示:
\[\mathbf{f}_k = \sum_{i\in\mathcal{I}} \tilde{m}_{ki}\mathbf{x}_i,\]其中 \(\mathbf{x}_i\) 是像素 \(p_i\) 的特征, \(\tilde{m}_{ki}\) 是归一化过(spatial softmax)的像素 \(p_i\) 属于 object \(k\) 的权重.
5.2 OCR
计算 pixel 的特征到 object 特征的关系:
\[w_{ik} = \frac{e^{\kappa(\mathbf{x}_i, \mathbf{f}_k)}}{\sum_{j=1}^K e^{\kappa(\mathbf{x}_i, \mathbf{f}_j)}}\]其中 \(\kappa(\mathbf{x}, \mathbf{f}) = \phi(\mathbf{x})\psi(\mathbf{f})\) 用于计算两个特征向量的相似度, \(\phi, \psi\) 为变换函数, 实现为 \(1\times1 \text{ conv} \rightarrow \text{BN} \rightarrow \text{ReLU}\).
然后通过公式 \(\eqref{eq:ocr}\) 计算 \(p_i\) 的 OCR 表示 \(\mathbf{y}_i\).
5.3 增广的特征表示
最后把像素 \(p_i\) 原来的特征和 OCR 特征拼接起来作为增广的特征表示:
\[\mathbf{z}_i = g(\text{cat}(\mathbf{x}_i, \mathbf{y}_i)),\]其中 \(\text{cat}(\cdot,\cdot)\) 为拼接操作, \(g(\cdot)\) 为变换函数.
6. Criss-Cross Attention (CCA)
由于 Self-Attention 需要计算特征图中所有 pixel 之间的关系, 所以需要 \(\mathcal{O}(N^2)\) 的复杂度, \(N\) 为特征图的大小. CCNet6 为降低计算复杂度, 提出了 CCA, 只在目标 pixel 的水平和垂直两个方向计算 attention, 然后循环两个 CCA 模块来实现全图的 attention.
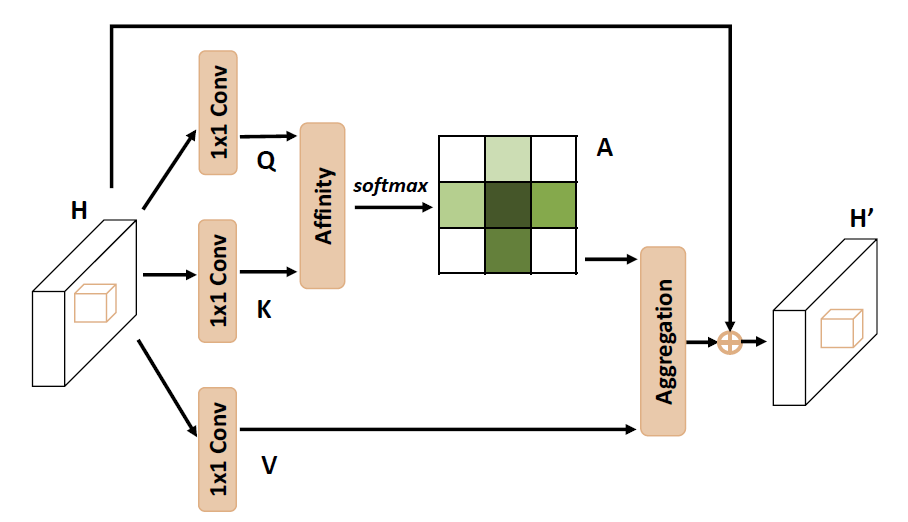
图 2. Illustrating the pipeline of CCA.
CCA 的复杂度为 \(\mathcal{O}(N\sqrt{N})\).
参考文献
-
Non-local neural networks>
Xiaolong Wang, Ross Girshick, Abhinav Gupta, Kaiming He
[html] In CVPR 2018 ↩ -
DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs
Liang-Chieh Chen, George Papandreou, Iasonas Kokkinos, Kevin Murphy, and Alan L Yuille.
[html]. In TPAMI 2017. ↩ -
Pyramid Scene Parsing Network
Hengshuang Zhao, Jianping Shi, Xiaojuan Qi, Xiaogang Wang, Jiaya Jia
[html] In CVPR 2017 ↩ -
Attention is all you need
Ashish Vaswani, Noam Shazeer, Niki Parmar, Jakob Uszkoreit, Llion Jones, Aidan N. Gomez, Lukasz Kaiser, Illia Polosukhin
[html] In NeurIPS 2017 ↩ -
Segmentation Transformer: Object-Contextual Representations for Semantic Segmentation
Yuhui Yuan, Xiaokang Chen, Xilin Chen, and Jingdong Wang
[html] In ECCV 2020 ↩ -
CCNet: Criss-Cross Attention for Semantic Segmentation>
Zilong Huang, Xinggang Wang, Yunchao Wei, Lichao Huang, Humphrey Shi, Wenyu Liu, Thomas S. Huang
[html] In ICCV 2019 and TPAMI 2020 ↩