- 1. Introduction
- 2. Problem Definitions
- 3. Useful Datasets
- 4 Meta-Learning Algorithms
- 5. Meta-Learning Application
- References
1. Introduction
机器学习算法通常需要大规模、多样的数据 + 大容量模型来实现较广的泛化性.
- ImageNet (Russakovsky et al., IJCV 2014)1 数据集上, Efficient Net (Tan and Le, ICML 2019)2 使用 88M 参数达到了 SOTA 84.4% top-1 / 97.1% top-5 的准确率 (监督学习, supervised learning).

图 1. Imagenet
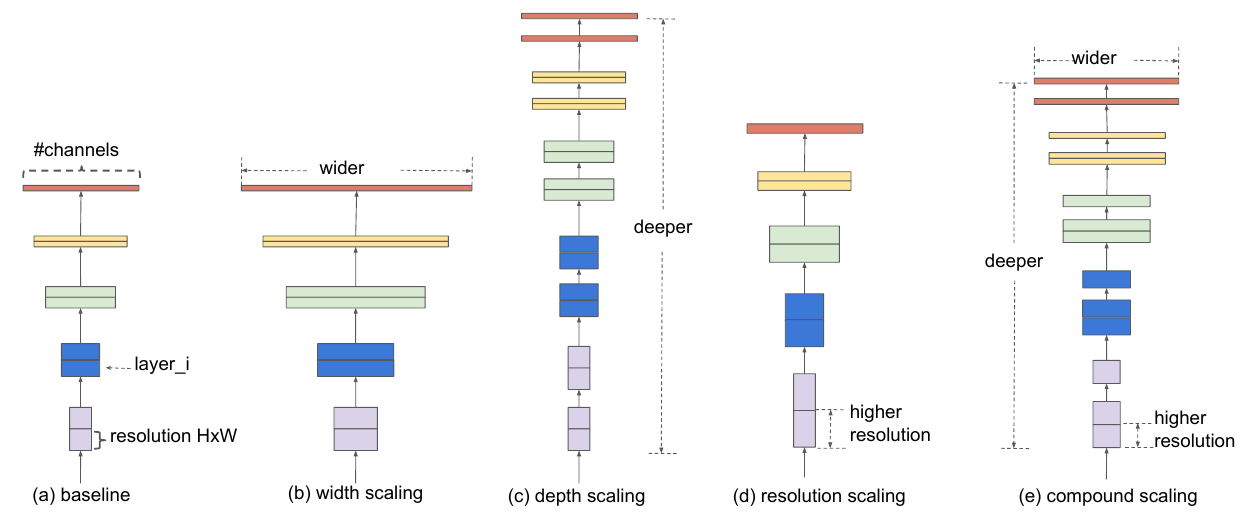
图 2. Efficientnet
Q: 如果没有这样的大规模数据集呢?
- 医学图像: CT, MRI, Ultrasound, X-ray
- 机器人技术 robotics
- 稀有语言的翻译 translation
- 推荐 recommendation
Q: 如果我们想得到一个通用 AI 系统呢?
- 需要不断地大量搜集新的数据, 学习并应用到新的任务上.
- 上个栗子:

图 3. 乔治·布拉克 vs 保罗·塞尚
Q: 人是如何识别图像的?
- 根据已有的经验, 临时创造了一个 Braque vs Cezanne 分类器
如何让机器完成这样的任务? 我们能否让机器从先前的经验中学到一种先验, 使得后续的学习变得更加容易?
-
训练一个模型, 可以根据不同的任务输出特定的分类器
-
Meta-learning: Learning to learn
Outline
- 问题定义 Problem Definitions
- 元学习算法 Meta-learning algorithms
- 黑盒适应 Black-box adaption
- 基于优化的推断 Optimization-based inference
- 非参方法/度量学习 Non-parametric methods / Metric learning
- 贝叶斯元学习 Bayesian meta-learning
- 元学习应用
2. Problem Definitions
监督学习:
\[\arg\max_{\phi}\log p(\phi\vert\mathcal{D})\qquad \mathcal{D}=\{(x_1, y_1), \dots, (x_k, y_k)\}\]考虑在监督学习中嵌入先验信息(如额外的数据):
\[\arg\max_{\phi}\log p(\phi\vert\mathcal{D}, \mathcal{D}_{\text{meta-train}}) \\ \mathcal{D}_{\text{meta-train}}=\{\mathcal{D}_1,\dots,\mathcal{D}_n\}\qquad \mathcal{D}_i=\{(x_1^i, y_1^i),\dots,(x_{k_i}^i, y_{k_i}^i)\}\]2.1 Meta-Learning Problem
额外的数据 \(\mathcal{D}_{\text{meta-train}}\) 作为先验信息可以提取为抽象的但更有代表性的特征 \(\theta^{\star}\) , 然后结合目标任务的训练集训练参数 \(\phi^{\star}\), 公式如下:
\[\text { meta-learning: } \theta^{\star}=\arg \max _{\theta} \log p\left(\theta | \mathcal{D}_{\text {meta-train }}\right) \label{eq:meta-learning}\] \[\text { adaptation: } \phi^{\star}=\arg \max _{\phi} \log p\left(\phi | \mathcal{D}, \theta^{\star}\right) \label{eq:adap}\]其中 \(\eqref{eq:adap}\) 又可以写为 \(\phi^{\star}=f_{\theta^{\star}}(\mathcal{D}^{tr})\) .
我们希望元学习器 (meta-learner) 可以学会学习 (learning to learn), 即一个成熟的元学习器在少量样本的前提下拥有快速泛化到不同任务的能力, 如下图所示.

图 4. 元学习过程
那么如何训练这样的元学习器呢? 以分类任务为例:
| Common Classifier | Meta-Learner | |
|---|---|---|
| 训练集 | 包含多种类别 | 包含多种分类任务 |
| 测试样本 | 一个无标注的数据, 预测其类别 | 一个新的分类任务 (有少量的带标注数据, 要预测无标注的数据) |
| 学习 | 类内相似性和类间判别性 | 如何生成优秀的分类器 |
| 预测 | 测试样本的类别 | 新分类任务的分类器 |
训练元学习器就是学习 \(\theta\) 使得 \(\phi=f_{\theta}(\mathcal{D}^{tr}_i)\) 对于 \(\mathcal{D}^{ts}_i\) 来说是个好的分类器.
2.2 Meta-Learning Terminology
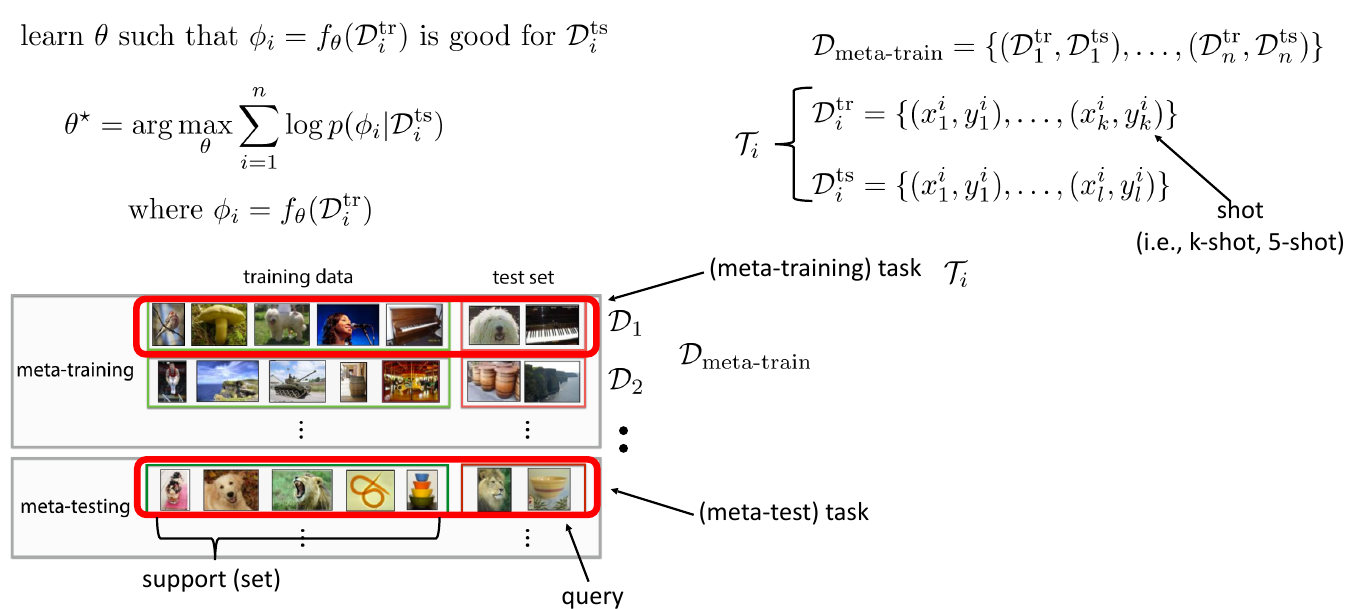
图 5. 元学习术语
3. Useful Datasets
- Omniglot dataset: 50 个字母表中的 1623 字符
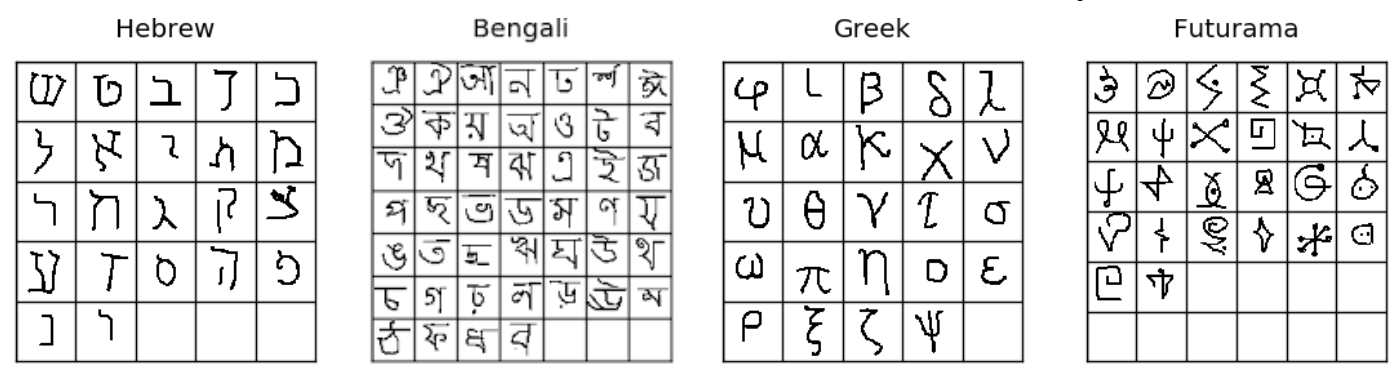
图 6. Omniglot 数据集
- MiniImageNet: 例如 5-way, 1-shot 图像分类

图 7. Mini-Imagenet 数据集
4 Meta-Learning Algorithms
- 选择如何对 adaptation 过程 \(p(\phi_i\vert\mathcal{D}^{tr}_i, \theta)\) 进行建模?
- 选择如何使用 \(\mathcal{D}_{\text{meta-train}}\) 优化 meta-learner 的参数 \(\theta\) ?
4.1 Black-Box Adaptation
Idea: 训练一个神经网络来表示 \(p(\phi_i\vert\mathcal{D}^{tr}_i, \theta)\). 我们先抛弃 \(\phi_i\) 的概率分布, 用神经网络来预测一个固定 \(\phi_i=f_{\theta}(\mathcal{D}^{tr}_i)\).
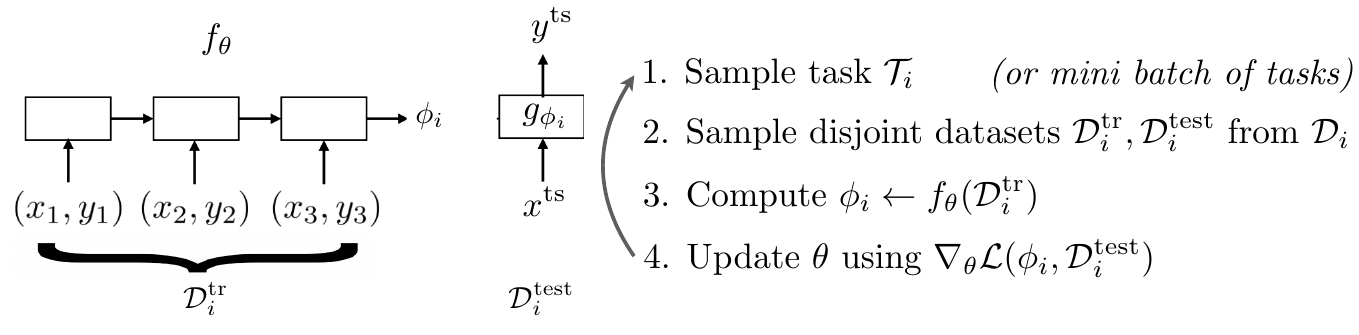
图 8. Black-Box Adaption
Q: 函数 \(f_{\theta}\) 的形式?
- LSTM
- Neural turing machine, NTM
- Self-attention
- Convolutions
Q: 上面的方法需要预测函数 \(g_{\phi_i}\) 的所有参数. 是否可以减轻负担?
- 只预测一个低维向量 \(h_i\) , 得到 \(\phi_i = \{h_i, \theta_g\}\) .
Q: 拓展性?
4.2 Optimization-based inference
Idea: Optimization as a model. 预测分类器参数的优化过程 (Ravi and Larochelle, ICLR 2017)3.
普通梯度更新 vs LSTM 的单元状态更新:
\[\begin{align} \theta_{t} &=\theta_{t-1}-\alpha_{t} \nabla_{\theta_{t-1}} \mathcal{L}_{t} \\ c_{t} &=f_{t} \odot c_{t-1}+i_{t} \odot \tilde{c}_{t} \end{align}\]类比 LSTM 的单元状态更新, 把分类器的优化过程作为模型来学习, 即训练元学习器预测缩放因子 \(f_t\) 和当前步的学习率 \(i_t\).
Idea: Meta parameters as initialization. 不直接预测分类器 \(g\) 的参数 \(\phi_i\) , 而是通过优化得到分类器. 使用元参数 \(\theta\) 作为分类器参数的初始化 initialization, 进行 fine-tune.
- 训练分类器 (fine-tune):
- 元学习 (meta-learning):
其中 \(\mathcal{D}^{tr}\) 是新任务的训练数据, \(\theta\) 是预训练的参数, 也是元学习器的参数. 这种基于优化的方式从元学习器获取分类器的方法成为 Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning, MAML (Finn et al., ICML 2017)4.
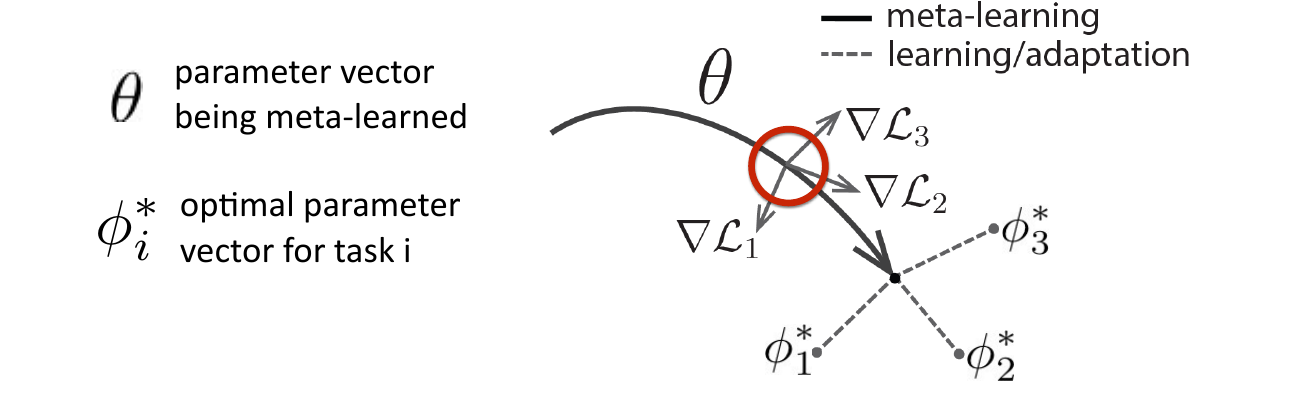
图 9. MAML
4.3 Non-parametric methods / Metric learning
Idea: 在小样本的条件下, 非参方法(用于分类)很简单, 并且通常表现的非常好.
- Meta-training: 参数化方法从大数据集中学习分类的概念, 并输出非参分类器
- Meta-test time: 使用非参分类器进行分类
非参方法最直接的做法就是把测试图像同训练图像作比较.
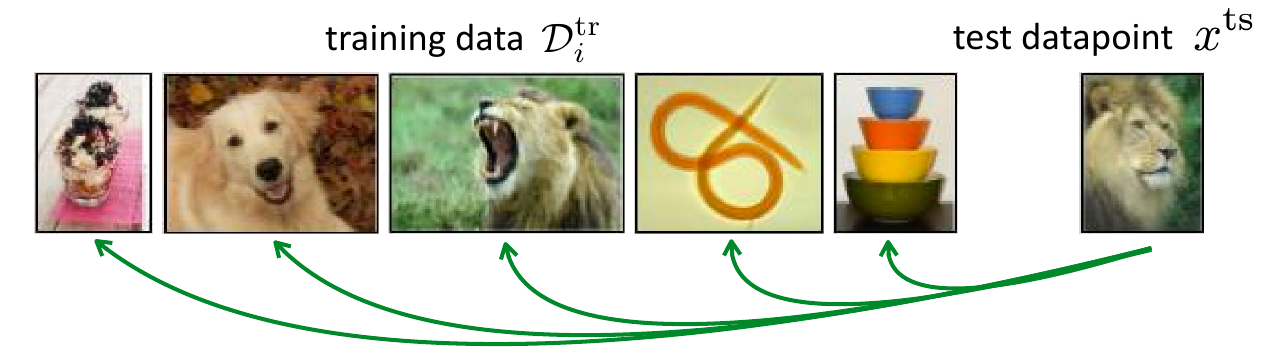
图 10. Comparison
Q: 如何训练非参方法的元学习器?

图 11. 训练元学习器 / Few-Shot Learning 训练
Q: 在什么样的空间中比较? 用什么度量比较?
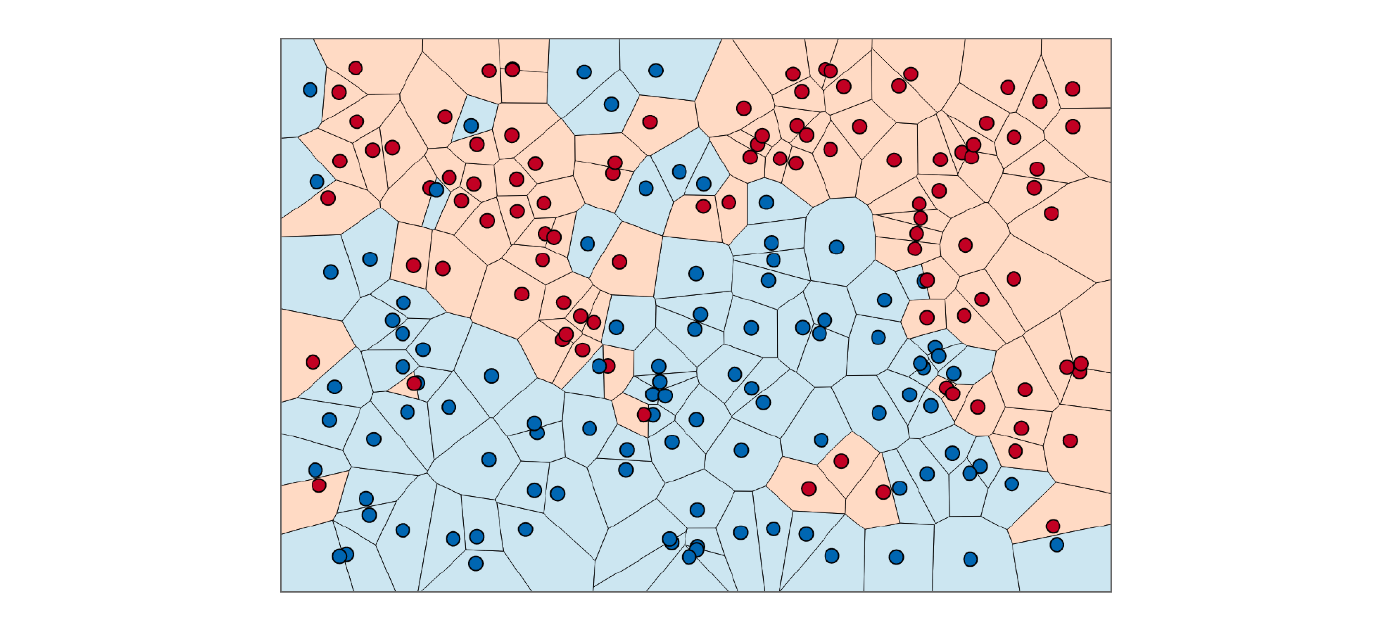
图 12. 特征空间中的样本点
- Siamese Network (Gregory Koch, ICML Deep Learning Workshop 2015)5
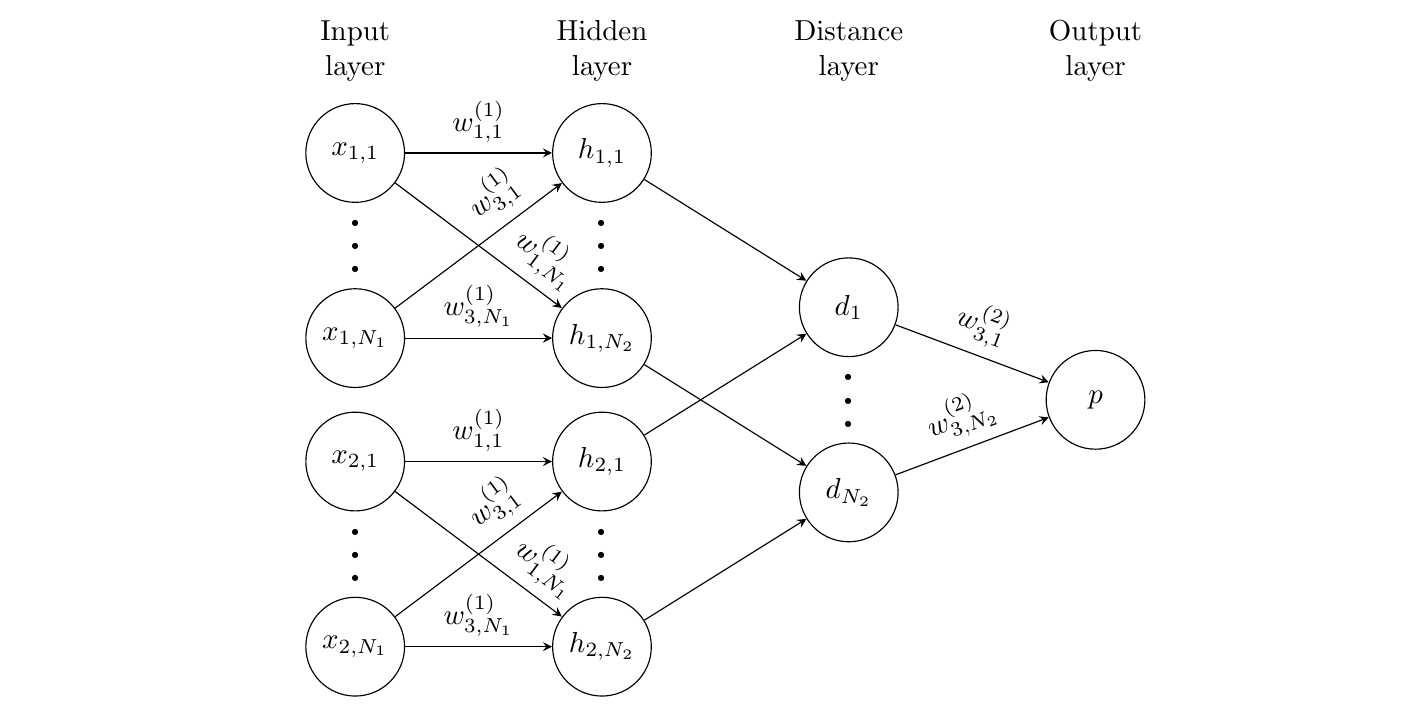
Meta-training: 2-way classification
Meta-test: N-way classification. 比较测试点和支撑集中所有的样本点
- Matching Networks (Vinyals et al., NeurIPS 2016)6
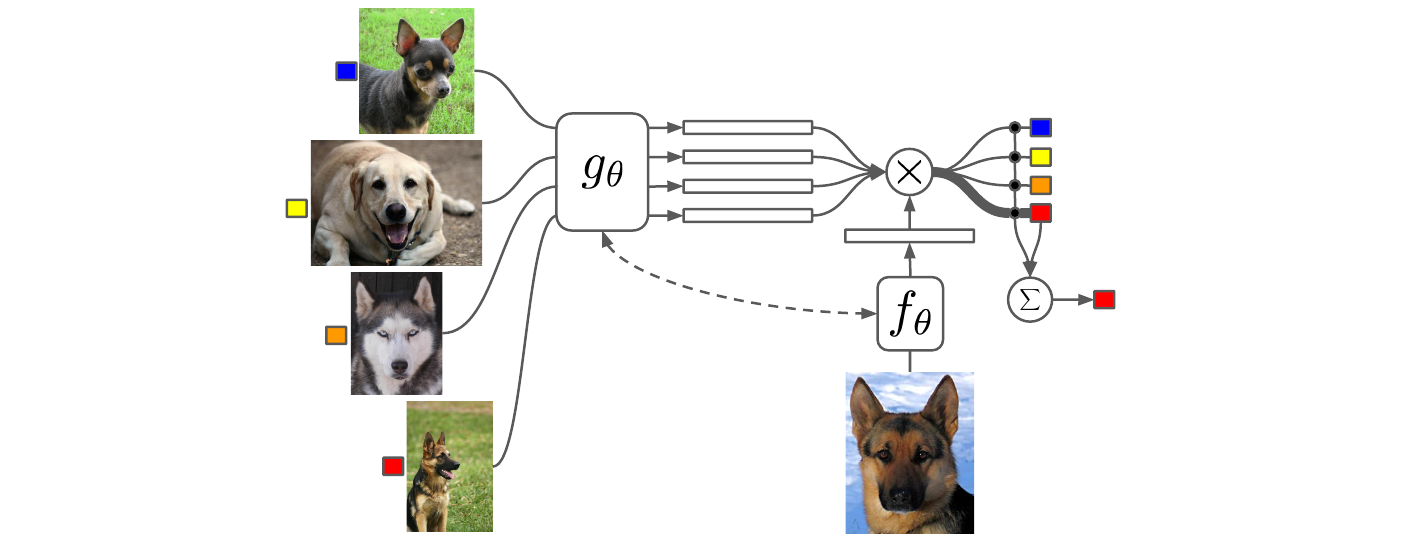
把 meta-training 和 meta-test 的模式匹配起来.
训练模型把样本点映射到一个 embedding space, 测试样本的标签由支撑集标签的加权平均得到. 这里使用了 attention 机制.
- Prototypical Networks (Snell et al., NeurIPS 2017)7
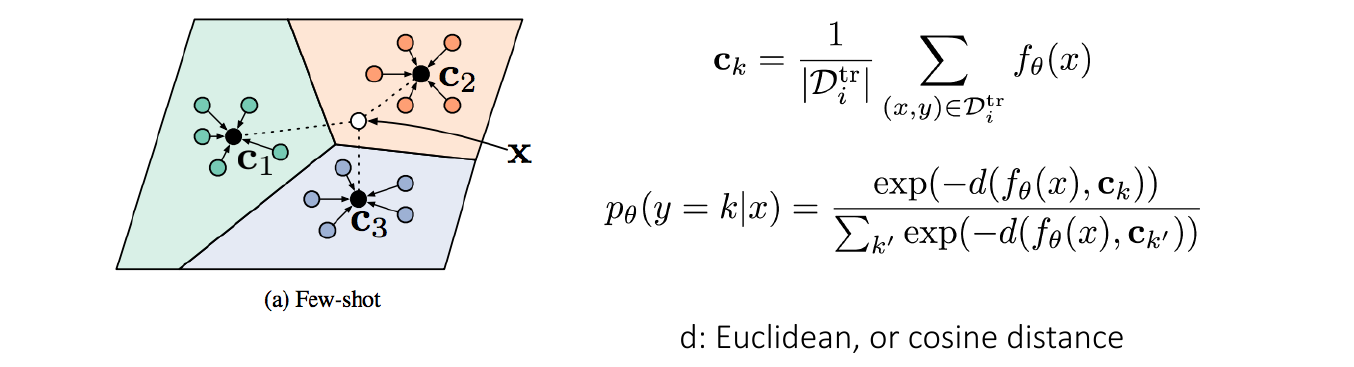
支撑集中每个类别的样本计算一个原型, 测试样本和原型计算距离进行分类.
- Relation Network (Sung et al., CVPR 2018)8
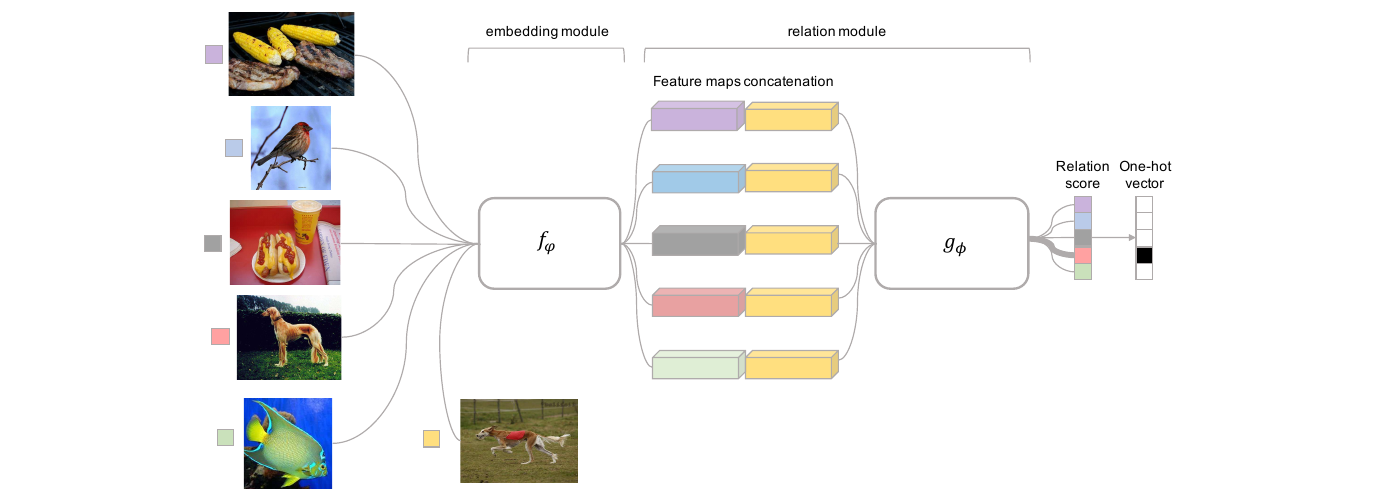
用什么度量比较: 欧氏距离, Cosine 距离, 更复杂的非线性函数(神经网络)
Position-Aware Relation Network (Wu et al., ICCV 2019)9
4.4 Bayesian meta-learning
分类器:
- 参数化方法: 使用 \(p(\phi_i\vert\mathcal{D}_i^{tr}, \theta)\) 的点估计
- 贝叶斯方法: 学习参数的分布 \(p(\phi_i\vert\mathcal{D}_i^{tr}, \theta)\) , 然后从分布中采样, 变分推断.
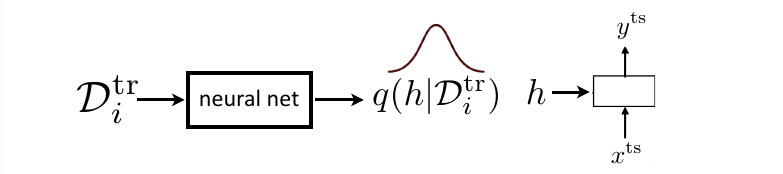
5. Meta-Learning Application
5.1 Few-Shot Image Classification
- Siamese Network
- Matching Network
- Prototypical Network
- Relation Network
5.2 Few-Shot Image Segmentation
- One-Shot Semantic Segmentation (Shaban et al., arxiv 2017)10
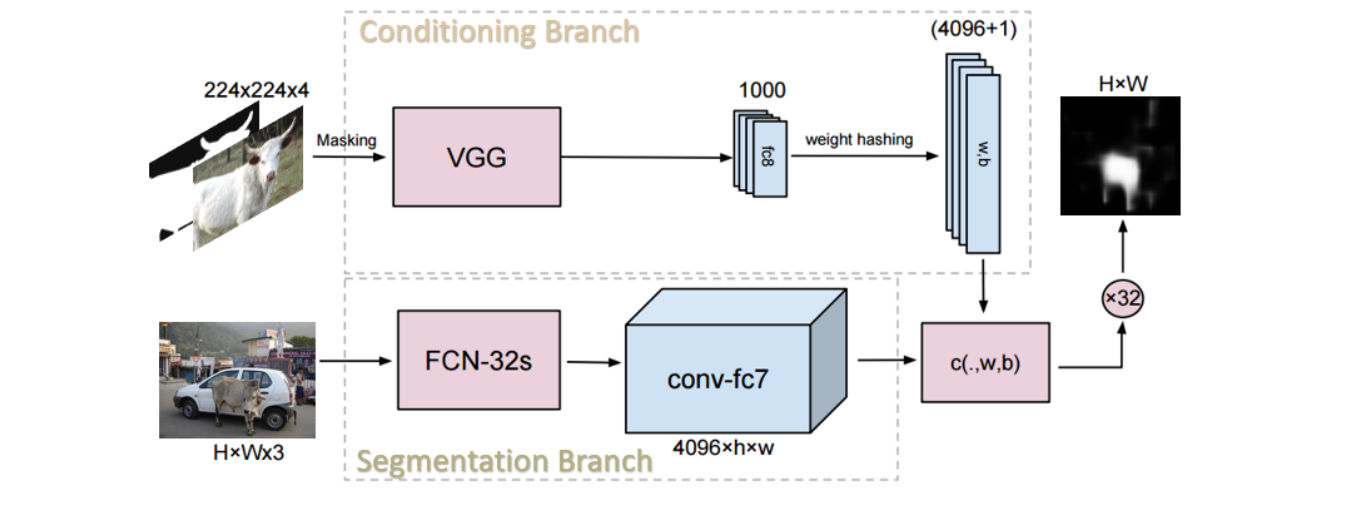
支撑集编码为特征向量, 与预测图像做像素级相似度对比. 本质上是 channel selection.
- Similarity guidance (Zhang et al., arxiv 2018)11
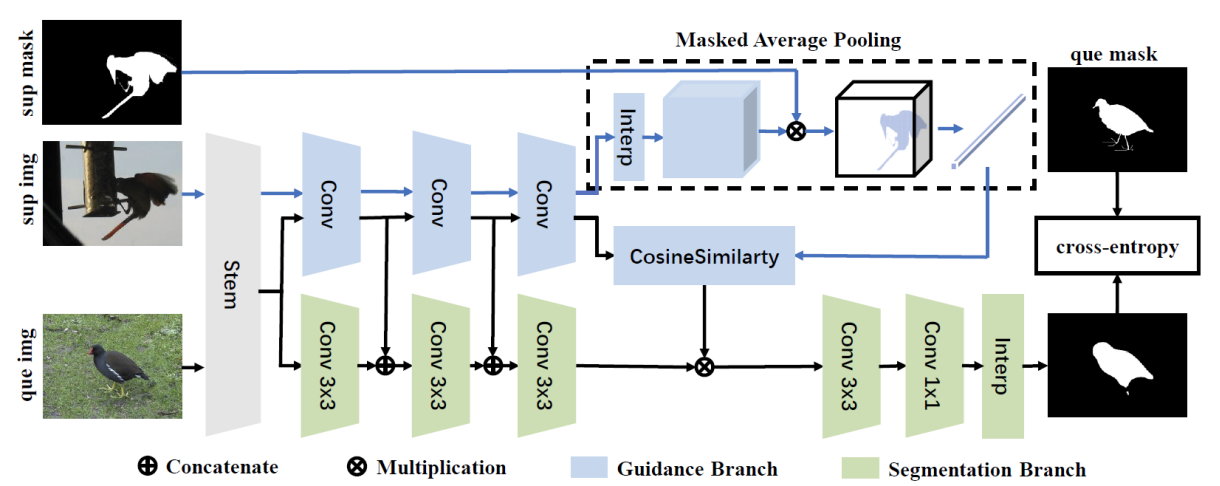
提出 masked average pooling (MAP), 对前景像素提取特征向量.
- Adaptive masked proxies (Siam et al., ICCV 2019)12
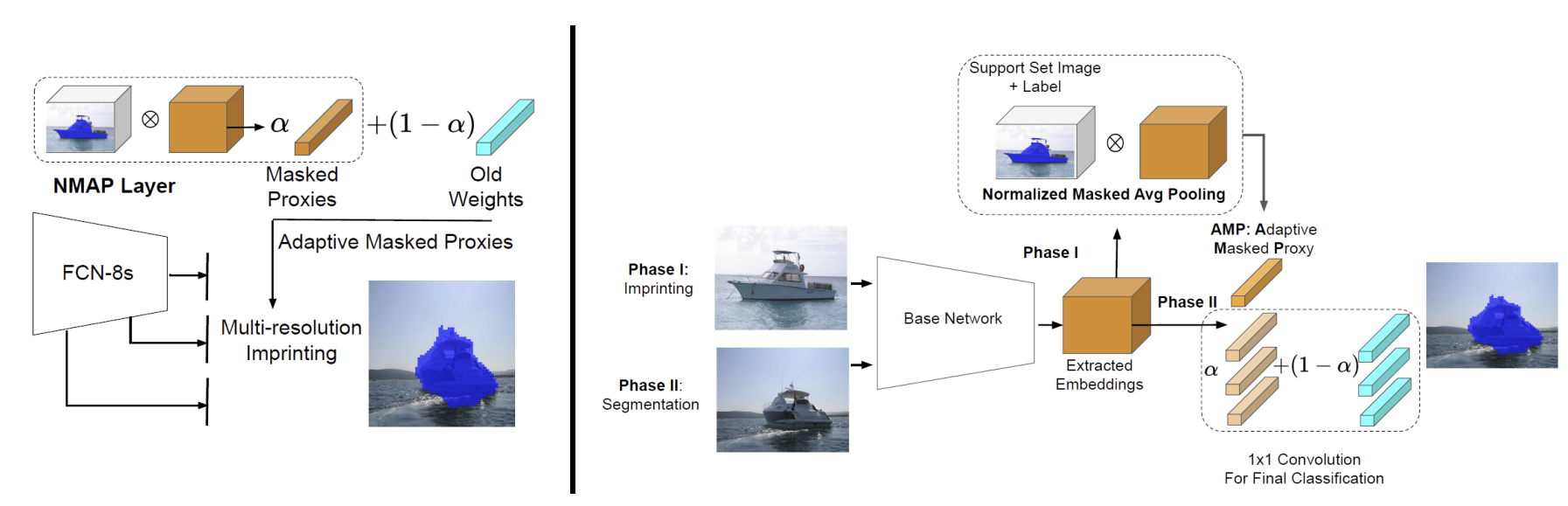
提出使用指数平均的方式更新 proxy / prototype.
提出了 Normalized MAP, NMAP, 把 weight imprinting (Qi et al., CVPR 2018)13 使用到了分割任务中.
\[\begin{align} \text{MAP + Cosine: } p(x_i\vert\theta)=\frac{\mathbf{v\cdot F}}{\Vert\mathbf{v}\Vert\cdot\Vert \mathbf{F}_i\Vert} \\ \text{NMAP + Imprint: } p(x_i\vert\theta)=\frac{\mathbf{v}}{\Vert\mathbf{v}_i\Vert}\cdot\mathbf{F}_i \\ \end{align}\]PS: 这篇都没有跟上一篇(MAP)比较.
- Attention-based multi-context (Hu et al., AAAI 2019)14
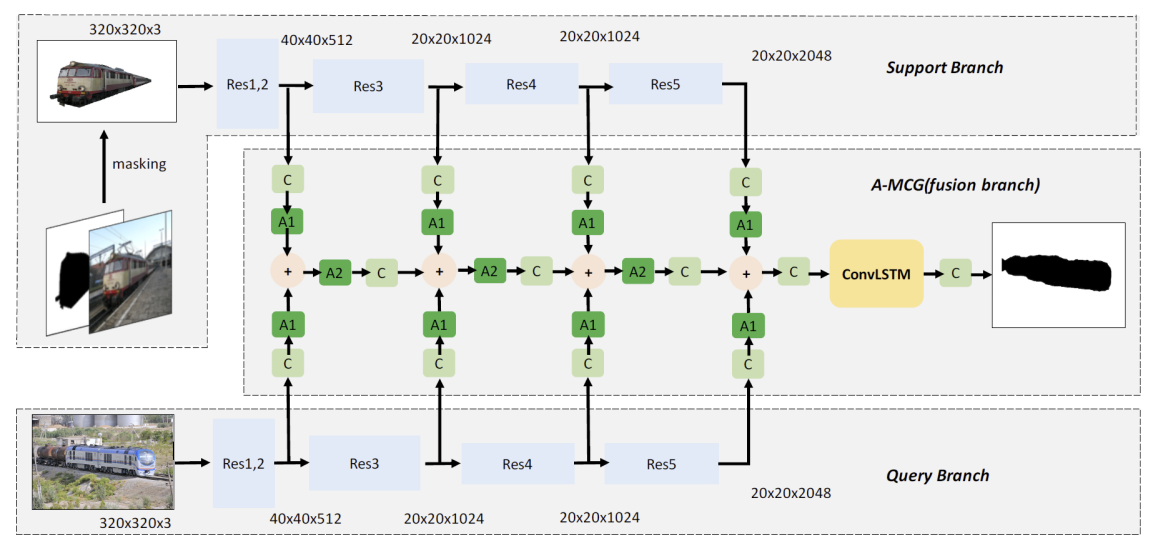
采用 ConvLSTM 融合 K-shot 的特征向量
采用 Attention
采用 multi-context
- Prototype alighment, PANet (Wang et al., ICCV 2019)15
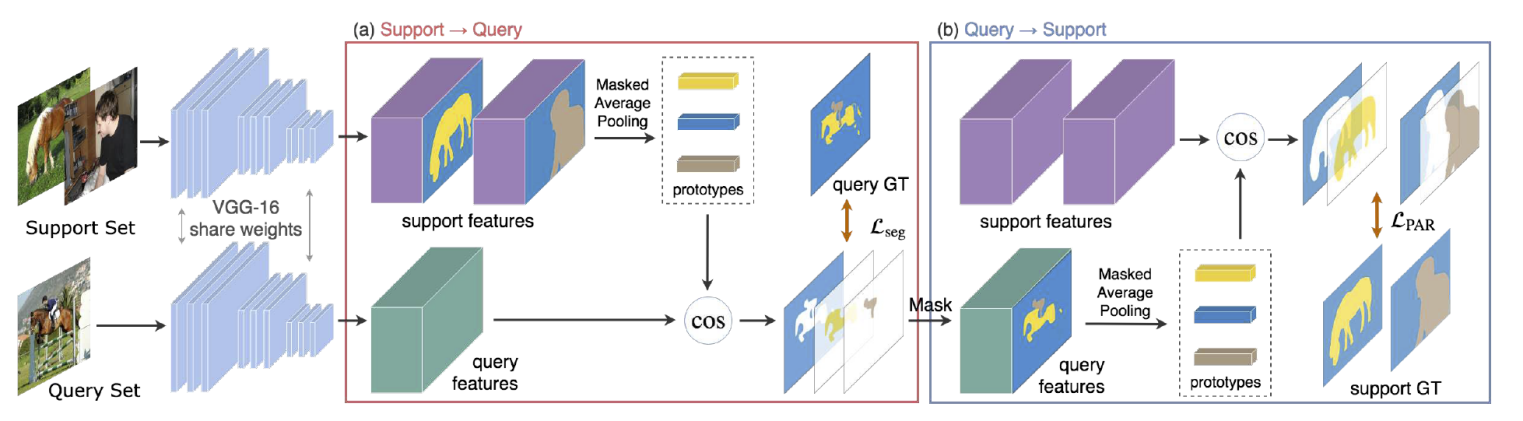
Sup –> Que 检索 + Que –> Sup 检索
5.3 Others
- Human motion and pose prediction
- Domain adaption
- Few-shot image generation
- Few-shot image-to-image translation
- Generation of novel viewpoints
- Generating talking heads from images
- Reinforcement learning
- One-shot imitation learning
References
-
ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge
Olga Russakovsky, Jia Deng, Hao Su et al.
[link]. In IJCV vol 115, 2015 ↩ -
EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks
Mingxing Tan, Quoc Le
[link]. In ICML 2019 ↩ -
Optimization As a Model For Few-Shot Learning
Sachin Ravi and Hugo Larochelle
[link]. In ICLR 2017 ↩ -
Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning for Fast Adaptation of Deep Networks
Chelsea Finn, Pieter Abbeel, Sergey Levine
[link]. In ICML 2017 ↩ -
Siamese neural networks for one-shot image recognition
Gregory Koch, Richard Zemel, Ruslan Salakhutdinov
[link]. In ICML Deep Learning Workshop 2015 ↩ -
Matching Networks for One Shot Learning
Oriol Vinyals, Charles Blundell, Timothy Lillicrap, koray kavukcuoglu, Daan Wierstra
[link]. In NeurIPS 2016 ↩ -
Prototypical Networks for Few-shot Learning
Jake Snell, Kevin Swersky, Richard Zemel
[link]. In NeurIPS 2017 ↩ -
Learning to Compare: Relation Network for Few-Shot Learning
Flood Sung, Yongxin Yang, Li Zhang, Tao Xiang, Philip H.S. Torr, Timothy M. Hospedales
[link]. In CVPR 2018 ↩ -
PARN: Position-Aware Relation Networks for Few-Shot Learning
Ziyang Wu, Yuwei Li, Lihua Guo, Kui Jia
[link]. In ICCV 2019 ↩ -
One-Shot Learning for Semantic Segmentation
Amirreza Shaban, Shray Bansal, Zhen Liu, Irfan Essa, Byron Boots
[link]. In arxiv 1709.03410 ↩ -
SG-One: Similarity Guidance Network for One-Shot Semantic Segmentation
Xiaolin Zhang, Yunchao Wei, Yi Yang, Thomas Huang
[link]. In arxiv 1810.09091 ↩ -
AMP: Adaptive Masked Proxies for Few-Shot Segmentation
Mennatullah Siam, Boris N. Oreshkin, Martin Jagersand
[link]. In ICCV 2019 ↩ -
Low-Shot Learning With Imprinted Weights
Hang Qi, Matthew Brown, David G. Lowe
[link]. In CVPR 2019 ↩ -
Attention-Based Multi-Context Guiding for Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation
Tao Hu, Pengwan Yang, Chiliang Zhang, Gang Yu, Yadong Mu, Cees G. M. Snoek
[link]. In AAAI 2019 ↩ -
PANet: Few-Shot Image Semantic Segmentation With Prototype Alignment
Kaixin Wang, Jun Hao Liew, Yingtian Zou, Daquan Zhou, Jiashi Feng
[link]. In ICCV 2019 ↩